目录
前言
对于Application,Activity和Service这几个类,我们是很[熟悉]的。确实[熟悉],作为App开发这基本都要面对这几个类。
比较好奇的朋友会发现,他们都拥有Context,但他们的Context有似乎有一点点的不同。今天有空,根据网上大佬的步伐,在这里简单记录一下。
正文
Context的使用场景
使用Context调用方法,比如启动Activity、访问资源、调用系统级服务等。
调用方法时传入Context,比如弹出Toast、创建Dialog等。
Context意为[上下文],也是Application,Activity和ServiceContext的祖先类。
Application -> ContextWrapper -> Context; Activity -> ContextThemeWrapper -> ContextWrapper -> Context Service -> ContextWrapper -> Context
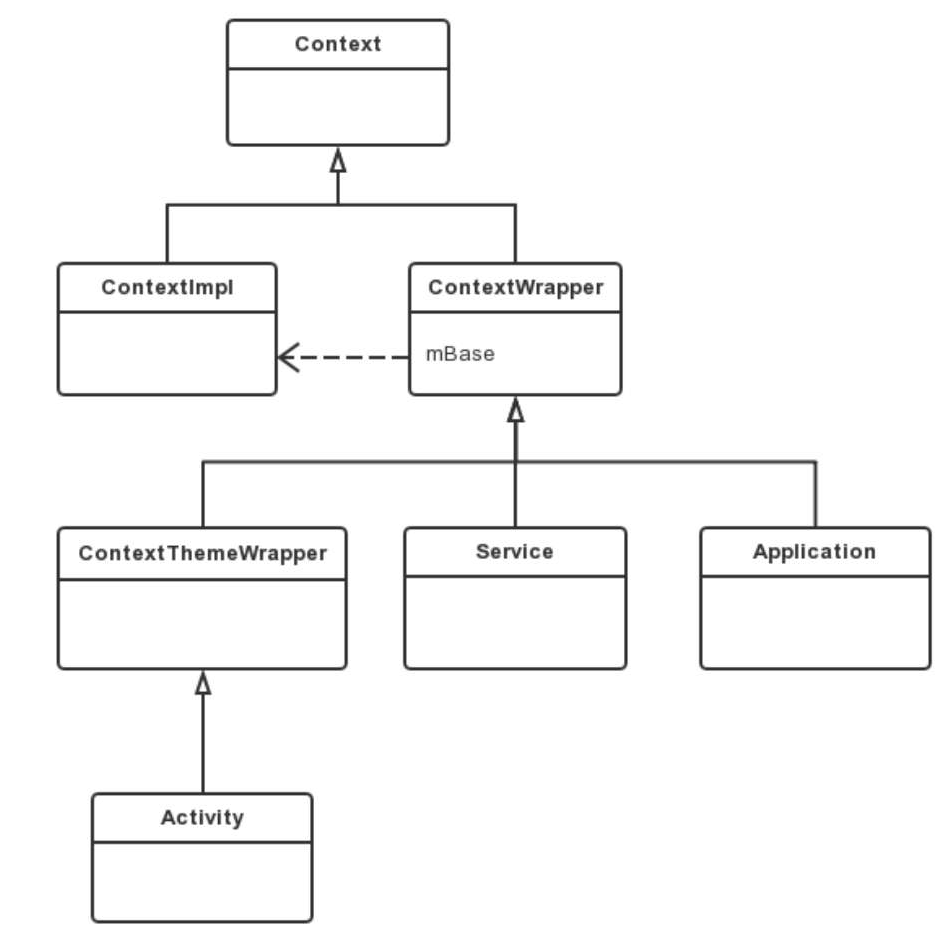
通过源码发现,Context其实也不干活的,具体干活的是ContextImpl。
今天介绍Activity的Context
Activity的Context
之前的源码分析《》,知道ActivityThread.java中给Activity创建Context。
ActivityThread.java
大部分代码省略
handleLaunchActivity()
public Activity handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, PendingTransactionActions pendingActions, Intent customIntent) { //略 final Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); //略 return a; }
performLaunchActivity()
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) { //略 //创建ContextImpl对象 ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r); Activity activity = null; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader(); //创建Activity对象,就是要启动的Activity activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity( cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent); //略 } catch (Exception e) { //略 } try { //创建Application //makeApplication()中会判断mApplication是否为null,不为null直接返回mApplication Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation); if (activity != null) { //略 //把activity赋值给mOuterContext appContext.setOuterContext(activity); //activity绑定appContext activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config, r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback); //略 //r.isPersistable()为false if (r.isPersistable()) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { //执行onCreate()流程 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state); } //略 r.activity = activity; } r.setState(ON_CREATE); mActivities.put(r.token, r); } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) { throw e; } catch (Exception e) { //略 } return activity; }
上面关注点
1. createBaseContextForActivity(); 2. appContext.setOuterContext(); 3. activity.attach();
下面进入简单介绍
createBaseContextForActivity()
private ContextImpl createBaseContextForActivity(ActivityClientRecord r) { //略 //ContextImpl的createActivityContext()进行创建 ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createActivityContext( this, r.packageInfo, r.activityInfo, r.token, displayId, r.overrideConfig); //略 return appContext; }
最后调用ContextImpl()构造函数
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, activityInfo.splitName, activityToken, null, 0, classLoader);
ContextImpl.java
appContext.setOuterContext()
在ContextImpl.java中,这里是把activity赋值给mOuterContext
final void setOuterContext(Context context) { mOuterContext = context; }
这里要知道的是mOuterContext是当前Activity实例,不过,这里并没有啥用处,可以略过。(仅记录一下)
Activity.java
attach()
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread, Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident, Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id, NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances, Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) { //[重]context绑定baseContext attachBaseContext(context); mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/); //创建Activity的PhoneWindow mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback); mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this); mWindow.setCallback(this); mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this); mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this); //略 }
attachBaseContext()
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
//调用父类的
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
if (newBase != null) {
newBase.setAutofillClient(this);
}
}
ContextThemeWrapper.java
attachBaseContext()
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
}
ContextWrapper.java
attachBaseContext()
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
//mBase为null
if (mBase != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
从这里看Activity和Application中的mBase不是一个变量,要不然mBase不为null了。如果不为null就会抛出异常!
参考文章
《Android进阶解密-刘望舒》
《Android内核剖析-柯元旦》
《》
© 版权声明

