目录
前言
对于Application,Activity和Service这几个类,我们是很[熟悉]的。确实[熟悉],作为App开发这基本都要面对这几个类。
几天记录一下Service的Context创建,其实也就是简单的说说。
正文
Context的使用场景
使用Context调用方法,比如启动Activity、访问资源、调用系统级服务等。
调用方法时传入Context,比如弹出Toast、创建Dialog等。
Context意为[上下文],也是Application,Activity和ServiceContext的祖先类。
Application -> ContextWrapper -> Context; Activity -> ContextThemeWrapper -> ContextWrapper -> Context Service -> ContextWrapper -> Context
或者看图,图上更详细
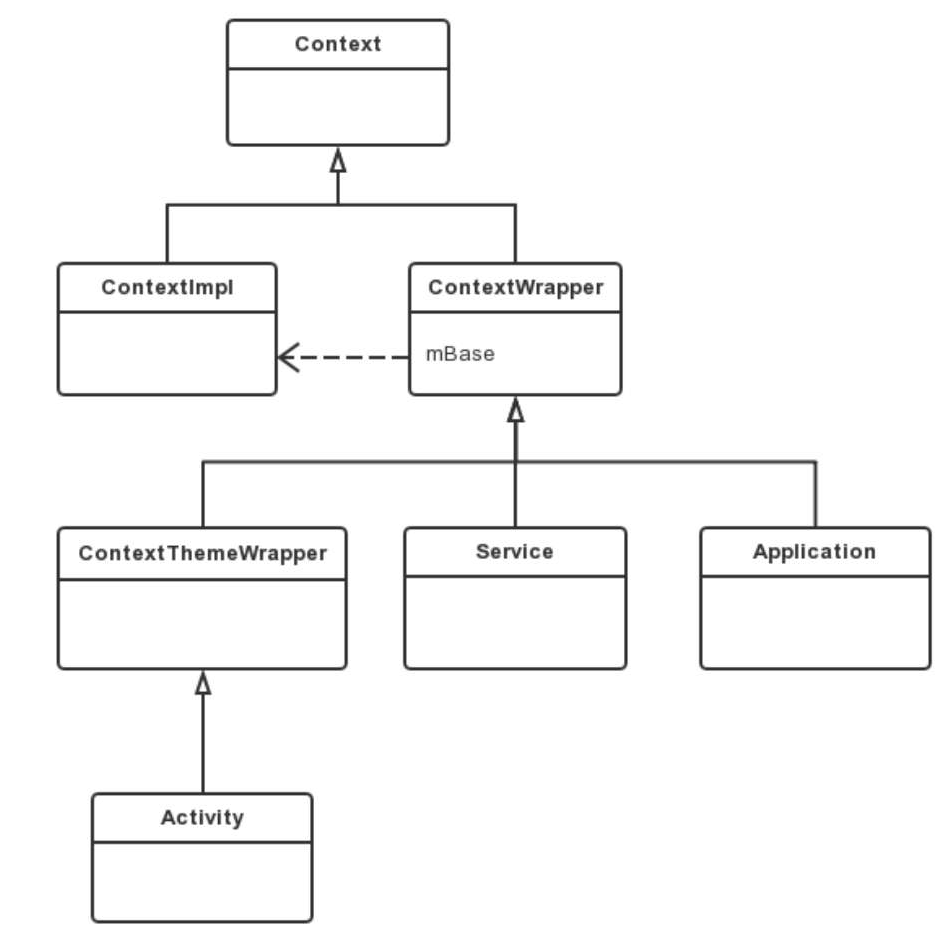
通过源码发现,Context其实也不干活的,具体干活的是ContextImpl。
今天就介绍一下Service的Context。
这部分在《》介绍了,而且Service的Context创建跟《》一样的。
不过为了单独记录,这里也单独抽出来说一下。(反正流水文,凑个字数)
接《》,进程创建成功后,ActivityThread.main()–>attach()–>ActivityManagerService.attachApplication()。
我们从ActivityManagerService.java中开始跟。
ActivityManagerService.java
attachApplication()
@Override public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread, long startSeq) { synchronized (this) { //略 attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid, callingUid, startSeq); //略 } }
attachApplicationLocked()
@GuardedBy("this") private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread, int pid, int callingUid, long startSeq) { //略 final String processName = app.processName; try { AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(app, pid, thread); //binder死亡监听 thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0); app.deathRecipient = adr; } catch (RemoteException e) { app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats); startProcessLocked(app, "link fail", processName); return false; } //略 try { //略 //isolatedEntryPoint为null if (app.isolatedEntryPoint != null) { thread.runIsolatedEntryPoint(app.isolatedEntryPoint, app.isolatedEntryPointArgs); } else if (app.instr != null) { //略 } else { //[重1]绑定bindApplication //通过Handler处理,主要是执行Application的onCreate()方法。 //这里不会阻塞!!! thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo, null, null, null, testMode, mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation, isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent, new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat, getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated), mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(), buildSerial, isAutofillCompatEnabled); } //略 } catch (Exception e) { //略 return false; } //略 boolean badApp = false; boolean didSomething = false; //启动Activity if (normalMode) { try { //重点启动Activity相关 if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) { didSomething = true; } } catch (Exception e) { badApp = true; } } //启动服务 if (!badApp) { try { //[重2],启动服务 didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName); checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after mServices.attachApplicationLocked"); } catch (Exception e) { badApp = true; } } //启动广播 if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) { try { //重点 didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app); } catch (Exception e) { badApp = true; } } //略 return true; }
这个attachApplicationLocked()很重要。
创建Application
如果需要,启动Activity
如果需要,启动Service
如果需要,发送广播(应该是静态广播,暂时没跟,后续分析)
这里我们关注Service的启动
if (!badApp) { try { didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName); } catch (Exception e) { badApp = true; } }
ActiveServices.java
attachApplicationLocked()
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord proc, String processName) throws RemoteException { boolean didSomething = false; //Pending中的服务,这里大于0 if (mPendingServices.size() > 0) { ServiceRecord sr = null; try { for (int i=0; i<mPendingServices.size(); i++) { sr = mPendingServices.get(i); //sr就是上面保存的Service信息 //ServiceRecord{66fcbc0 u0 com.biumall.biuaidlserver/.server.DemoService} if (proc != sr.isolatedProc && (proc.uid != sr.appInfo.uid || !processName.equals(sr.processName))) { continue; } //找到了,先移除mPendingServices mPendingServices.remove(i); i--; proc.addPackage(sr.appInfo.packageName, sr.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats); //[重]启动服务,看包名就知道啥意思哈 realStartServiceLocked(sr, proc, sr.createdFromFg); didSomething = true; if (!isServiceNeededLocked(sr, false, false)) { bringDownServiceLocked(sr); } } } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e; } } //重新启动的服务为0 if (mRestartingServices.size() > 0) { //略 } return didSomething; }
realStartServiceLocked()
哈哈,命名给力,但,也是调用ActivityThread来创建。。
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException { //略 //记录是否创建成功 boolean created = false; try { //略 //创建服务的启动 app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo, mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo), app.repProcState); r.postNotification(); //只要不异常,这里表示创建成功 created = true; } catch (DeadObjectException e) { mAm.appDiedLocked(app); throw e; } finally { //略 } //略 }
这里只关注服务的创建,其他的不关心哈。
ActivityThread.java
scheduleCreateService()
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) { updateProcessState(processState, false); CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData(); s.token = token; s.info = info; s.compatInfo = compatInfo; //发送CREATE_SERVICE sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s); }
handleMessage()
case CREATE_SERVICE: //处理创建服务 handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);1 break; case BIND_SERVICE:
handleCreateService()
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) { //略 //获取LoadedApk对象 LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck( data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo); Service service = null; try { java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); //创建Service对象 service = packageInfo.getAppFactory() .instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent); } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } try { //创建Service的Context ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo); //这里也赋值了 context.setOuterContext(service); //创建Application[仅仅获取而已,之前有创建过] Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation); //service 绑定context service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app, ActivityManager.getService()); //调用Service的onCreate() service.onCreate(); mServices.put(data.token, service); try { ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting( data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } catch (Exception e) { if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to create service " + data.info.name + ": " + e.toString(), e); } } }
这才是真正的创建Service。
创建Service
创建ContextImpl
service.attach()
调用service.onCreate()
跟Activity一样的方式。
至此,Service的Context也创建完成了。
参考文章
《

